European Parliament election, 2009
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| All 736 seats to the European Parliament and 18 observers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First party | Second party | Third party | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
| Leader | Joseph Daul | Martin Schulz | Graham Watson | |||
| Party | UMP | SPD | Liberal Democrat | |||
| Alliance | EPP | S&D | ALDE | |||
| Leader since | 9 January 2007 | 5 July 2004 | 13 July 2004 | |||
| Leader's seat | East France | Germany | South West England | |||
| Last election | 277 seats, 34.1% | 218 seats, 25.8% | 106 seats, 12.7% | |||
| Seats won | 265 at least 6 observers |
183 at least 5 observers |
84 | |||
| Seat change | -12 | -35 | -22 | |||
|
|
||||||
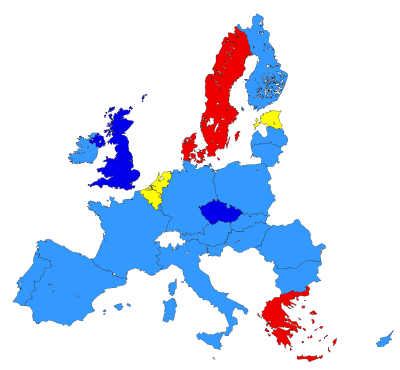
| The largest European Parliament group (Caucus) as elected by each of the member states: Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats
Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe European People's Party European Conservatives and Reformists |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
||||||
| European Union |
 This article is part of the series: |
|
Policies and issues
|
|
Foreign relations
|
Elections to the European Parliament were held in the 27 member states of the European Union (EU) between 4 and 7 June 2009.[1][2] A total of 736 Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) were elected to represent some 500 million[3] Europeans, making these the biggest trans-national elections in history. An additional 18 observers ("virtual MEPs") were (supposed to be) pre-elected.
Contents |
Overview
The majority of MEPs were elected on Sunday 7 June, but because of traditional polling days varying from country to country according to local custom, some countries held their elections in the three preceding days:
- Thursday 4 June: United Kingdom (including Gibraltar), Netherlands (including Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles)[4]
- Friday 5 June: Ireland, Czech Republic (day 1)
- Saturday 6 June: Cyprus, France (for part of Outre-mer),[5] Italy (day 1), Latvia, Malta, Slovakia, Czech Republic (day 2)
- Sunday 7 June: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Denmark, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Hungary, Italy (day 2), Lithuania, Luxembourg, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Sweden
In seven EU member-states, other votes occurred alongside the elections to the European Parliament: a general election in Luxembourg; local government elections in Latvia,[6] part of the United Kingdom,[7] parts of Germany, Italy, Malta, and Ireland[8] (as well as two by-elections in Dublin South and Dublin Central); regional elections in Belgium; and a referendum on reforming the succession law in the Kingdom of Denmark that would give women the same rights through equal primogeniture.
This was the first European Parliament election that Bulgaria and Romania participated in at the same time as the other member states. When they joined the EU in 2007, they held elections for MEPs outside the normal electoral calendar.
Polls

A poll sampling nineteen national polls predicted the following results: EPP 265 MEPs, PES 195 MEPs, ALDE 95 MEPs, GUE–NGL 40 MEPs, Greens-EFA 35 MEPs, UEN 35 MEPs. The remaining 70 MEPs were not predicted, but about 20 were expected to be gained by far-right or Libertas candidates. IND/DEM was predicted to fade away due to Libertas' expected success.[9]
A prediction by political scientists Simon Hix (London School of Economics), Michael Marsh (Trinity College Dublin) and Nick Vivyan (London School of Economics) foresaw little change in the distribution of seats, predicting 249 seats for the EPP, 209 for the PES, 87 for ALDE, 58 for UEN or the European Conservatives, 48 for GUE–NGL, 39 for Greens–EFA, 17 for IND/DEM (resulting in its dissolution) and 29 NI; Libertas was not expected to win any seats.[10][11] A later prediction saw 262 seats for the EPP, 194 for the PES, 85 for ALDE, 53 for UEN or the European Conservatives, 40 for GUE–NGL, 50 for Greens–EFA, 23 for IND/DEM (resulting in its dissolution) and 29 NI.[12]
Constitutional issues
Re-apportionment of seats
At the previous election member states were granted a fixed allocation of seats for election as determined under the provisions of the Treaty of Nice (current allocation is in the 2007 column below). The admission of Bulgaria and Romania midway through the previous Parliament's term had increased the overall size of the assembly to 785, and under the terms of the Treaty of Nice it was mandated that the seat allocations be modified for this election, dropping 49 seats to keep the overall size of the Parliament down.
It had been the stated desire of the member-state governments to ratify the Treaty of Lisbon before the election so that its articles governing the European Parliament could enter force as of this election. However, this was blocked by the Irish rejection of the treaty in a referendum. Under Lisbon, there would be a somewhat different allocation of seats, with fewer seats eliminated, leading to a slightly different distribution totalling 751 MEPs. If the Lisbon Treaty is subsequently ratified, it is planned to give the additional seats to the "increasing" countries already before the next elections, bringing the number of MEPs to 754 for a transitional period until 2014.[13]
To have the additional MEPs ready at hand, 18 "phantom MEPs" were elected at the election. These will probably get observer status in the European Parliament and full payment from the day the Lisbon Treaty enters into force, but only become full members of parliament after an additional protocol is ratified.[14][15] The latter will require a decision by the European Council.[16]
| Member state | 2007 | 2009 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 99 | 99 | ±0 |
| Czech Republic | 24 | 22 | −2 |
| Slovakia | 14 | 13 | −1 |
| France | 78 | 72 | −6 |
| Greece | 24 | 22 | −2 |
| Ireland | 13 | 12 | −1 |
| Italy | 78 | 72 | −6 |
| Hungary | 24 | 22 | −2 |
| Lithuania | 13 | 12 | −1 |
| United Kingdom† | 78 | 72 | −6 |
| Portugal | 24 | 22 | −2 |
| Latvia | 9 | 8 | −1 |
| Spain | 54 | 50 | −4 |
| Sweden | 19 | 18 | −1 |
| Slovenia | 7 | 7 | ±0 |
| Poland | 54 | 50 | −4 |
| Austria | 18 | 17 | −1 |
| Cyprus | 6 | 6 | ±0 |
| Romania | 35 | 33 | −2 |
| Bulgaria | 18 | 17 | −1 |
| Estonia | 6 | 6 | ±0 |
| Netherlands | 27 | 25 | −2 |
| Finland | 14 | 13 | −1 |
| Luxembourg | 6 | 6 | ±0 |
| Belgium | 24 | 22 | −2 |
| Denmark | 14 | 13 | −1 |
| Malta | 5 | 5 | ±0 |
| Total: | 785 | 736 | −49 |
† – Includes Gibraltar, but not any of the other overseas territories or Crown dependencies.
Italicised countries are divided into sub-national constituencies.
Campaigning

Many of the national parties running in the election are affiliated to transnational pan-European political parties known as political parties at European level. Those pan-European parties are EPP, PES, ELDR, EFA, European Greens, AEN, PEL, EDP and EUD. The question of which was the first to campaign transnationally is the subject of some debate, with the European Greens stating that they were the first in 2004.[17] New parties that aspire to pan-European status during the 2009 elections include Newropeans, Europe United,[18] Europe – Democracy – Esperanto and Libertas Party Limited. The role for pan-European political parties has been expanded by changes enacted by the European Commission in 2007 under the direction of Margot Wallström.[19]
Four incumbent European Commissioners will run as candidates in the election: Viviane Reding (Luxembourg, information society & media, Christian Social People's Party/EPP), Louis Michel (Belgium, development & humanitarian aid, Reformist Movement/ELDR), Danuta Hübner (Poland, regional policy, Civic Platform/EPP), Meglena Kuneva (Bulgaria, consumer protection, National Movement for Stability and Progress/ELDR).[20] Ján Figeľ (Slovakia, education, training & culture, Christian Democratic Movement/EPP) was tipped to but ultimately did not run. He is bound to become the new chairman of his party instead.[21]
Kuneva later decided not to take up her seat in the European Parliament.[22]
Issue-based campaigns
These divide into EU-wide and nationally based campaigns, often by non-governmental organisations focussed on specific policy areas. They are designed to influence MEP candidates, those with a strong interest in the issue, and voters in general. Examples of nationally based campaigns include those of the Royal College of Nursing[23][24] and British Overseas NGOs for Development.[25][26]
Media coverage

The European Parliament, National broadcasters, the EBU, with the cooperation of the Communication Commissioner, Margot Wallström, are jointly working to make the 2009 election more interesting to the public and increase turnout. Previously, diverse news media in the European Union, and the fact that the election takes place over several days, have made it hard to attract viewers. The media consortium is hoping to focus the 2009 election more towards the EU level and the European Parliament itself, hoping to make the election more interesting and cosmetically appealing for television viewers.[27] Members of the European Parliament (MEP) also started initiatives in late 2007 to make the election more interesting to voters in a bid to increase turnout.[28]
From 1 April Parliament started putting up election posters, internet banners and billboards encouraging people to vote, with messages such as "How much should we tame financial markets?" to demonstrate the role of Parliament. The same 10 posters, designed by Berlin-based advertising company Scholz & Friends Group, were translated into all 23 languages and have been deployed across the whole of the EU. However, some posters are put up more in countries where the issues they present are of more significance and the most posters will be put up in those countries which had the lowest turnout in 2004. The end slogan is "Use your vote in the European Parliament Elections" with the date of the election in that country. The entire campaign costs 18 million euros, or 0.05 euros per eligible voter, with Germany, Spain and Italy donating some advertising space free of charge.[29]
Results
The national results as of 8 June 2009 are as follows. (based on predictions, to be confirmed)
Full MEPs (with pre-election group alignment)
736 members with full voting rights (the groups used are the groups they had been associated with directly prior to the elections):
| Political group
Country |
EPP | PES[30] | ALDE | Greens-EFA | EUL-NGL | UEN | ID | Other (incl. NI) |
MEPs | Turnout | Cite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 6 (ÖVP) | 4 (SPÖ) | 2 (Grüne) | 3 (Martin) 2 (FPÖ) |
17 | 45.97% | [31][32] [33] |
||||
| Belgium | 3 (CD&V) 1 (N-VA) 1 (CDH) 1 (CSP-EVP) |
3 (PS) 2 (SP.A) |
3 (OpenVLD) 2 (MR) |
1 (Green!) 2 (Ecolo) |
2 (VB) 1 (LDD) |
22 | 91% | [34] | |||
| Bulgaria | 5 (GERB) 1 (SDS/DSB) |
4 (BSP) | 3 (DPS) 2 (NDSV) |
2 (Attack) | 17 | 37.49% | [35][36] | ||||
| Cyprus | 2 (DISY) | 1 (EDEK) | 2 (AKEL) | 1 (DIKO) | 6 | 58.88% | [37][38] | ||||
| Czech Republic | 2 (KDU–ČSL) | 7 (ČSSD) | 4 (KSČM) | 9 (ODS) | 22 | 28.22% | [39][40] | ||||
| Denmark | 1 (C) | 4 (A) | 3 (V) | 2 (F) | 1 (N) | 2 (O) | 13 | 59.5% | [41] | ||
| Estonia | 1 (IRL) | 1 (SDE) | 1 (RE) 2 (KE) |
1 (Tarand) | 6 | 43.9% | [42][43] | ||||
| Finland | 3 (Kok.) 1 (KD) |
2 (SDP) | 3 (Kesk.) 1 (SFP) |
2 (Vihr.) | 1 (PS) | 13 | 40.3% | [45] | |||
| France | 24 (UMP) 3 (NC) 2 (LGM) |
14 (PS) | 6 (MoDem) | 14 (E-É) | 5 (FG) | 1 (Libertas) | 3 (FN) | 72 | 40.48% | [46][47] | |
| Germany | 34 (CDU) 8 (CSU) |
23 (SPD) | 12 (FDP) | 14 (Grüne) | 8 (Linke) | 99 | 43.3% | [48] | |||
| Greece | 8 (ND) | 8 (PASOK) | 1 (Greens) | 2 (KKE) 1 (SYRIZA) |
2 (LAOS) | 22 | 52.63% | [49] | |||
| Hungary | 14 (Fidesz-MPP) 1 (MDF) |
4 (MSZP) | 3 (Jobbik) | 22 | 36.28% | [50][51] | |||||
| Ireland | 4 (FG) | 3 (Lab) | 3 (FF) 1 (Harkin) |
1 (SP) | 12 | 57.6% | [52][53] | ||||
| Italy | 29 (PdL) 5 (UDC) 1 (SVP) |
7 (IdV) | 9 (LN) | 21 (PD) | 72 | 65.05% | [54][55] | ||||
| Latvia | 1 (JL) 2 (PS) |
1 (LPP/LC) | 1 (PCTVL) | 1 (TB/LNNK) | 2 (SC) | 8 | 52.57% | [56][57] | |||
| Lithuania | 4 (TS-LKD) | 3 (LSDP) | 1 (DP) 1 (LRLS) |
2 (TT) | 1 (LLRA) | 12 | 20.54% | [58] | |||
| Luxembourg | 3 (CSV) | 1 (LSAP) | 1 (DP) | 1 (déi gréng) | 6 | 91% | [59] | ||||
| Malta | 2 (PN) | 3 (PL) | 5 | 78.8% | [60][61] | ||||||
| Netherlands | 5 (CDA) | 3 (PvdA) | 3 (VVD) 3 (D66) |
3 (GL) | 2 (SP) | 2 (CU-SGP) | 4 (PVV) | 25 | 36.9% | [62] | |
| Poland | 25 (PO) 3 (PSL) |
7 (SLD-UP) | 15 (PiS) | 50 | 24.53% | [63][64] | |||||
| Portugal | 8 (PSD) 2 (CDS) |
7 (PS) | 2 (CDU) 3 (BE) |
22 | 36.77% | [65] | |||||
| Romania | 10 (PD-L) 2 (UDMR) 1 (Băsescu) |
11 (PSD-PC) | 5 (PNL) | 1 (Tőkés) | 3 (PRM) | 33 | 27.67% | [66] | |||
| Slovakia | 2 (SDKÚ-DS) 2 (KDH) 2 (SMK) |
5 (Smer) | 1 (SNS) 1 (LS-HZDS) |
13 | 19.63% | [67][68] | |||||
| Slovenia | 2 (SDS) 1 (NSi) |
2 (SD) | 1 (LDS) 1 (Zares) |
7 | 28.02% | [69][70] | |||||
| Spain | 23 (PP) | 21 (PSOE) | 1 (CDC) 1 (EAJ-PNV) |
1 (ERC) 1 (ICV) |
1 (IU) | 1 (UPyD) | 50 | 46.0% | [71][72] | ||
| Sweden | 4 (M) 1 (KD) |
5 (S) | 3 (FP) 1 (C) |
2 (MP) | 1 (V) | 1 (PP) | 18 | 45.53% | [73] | ||
| United Kingdom | 13 (Lab) | 11 (LD) | 2 (GPEW) 2 (SNP) 1 (PC) |
1 (SF) | 13 (UKIP) | 26 (Con/UCUNF) 2 (BNP) 1 (DUP) |
72 | 34.48% | [74][75] | ||
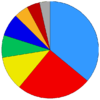
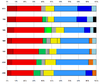
| Total | 264 | 161 | 83 | 53 | 33 | 14 | 18 | 110 | 736 | 43.24% | [76][77] |
| Political group | EPP | PES | ALDE | Greens-EFA | EUL-NGL | UEN | ID | Other (incl. NI) |
MEPs | Turnout | Cite |
| Previous total (unadjusted) |
288 (−24) | 217 (−56) | 100 (−17) | 43 (+10) | 41 (−8) | 44 (−30) | 22 (−4) | 30 (+80) | 785 (–49) | ||
| Previous total (adjusted) |
244 (+20) | 196 (−35) | 88 (−5) | 40 (+13) | 38 (−5) | 24 (−10) | 21 (−3) | 85 (+25) | 736 (±0) | ||
NB: "Adjusted" figures restate group numbers to proportionately reflect the reduction of the Parliament's size by 49, and to reflect the following political group movements announced prior to the election: DIKO (CY) from ALDE to Other; ODS (CZ) from EPP to Other; FF (IE) from UEN to ALDE; AN (IT) from UEN to EPP; PD (IT) from PES and ALDE to Other; PiS (PL) from UEN to Other; and Conservatives/UCUNF (UK) from EPP to Other.
Note:Postal votes missing from Slovenia. Complete results were supposed to be announced on 15 June
Role of the Treaty of Lisbon
It had initially been foreseen that the Treaty of Lisbon would have entered into force by the time of these elections, making them the first to be held under its provisions. However, primarily because of the failure of the referendum in Ireland, the framework established by the Treaty of Nice will be used again. Amongst other differences, the number of MEPs to be returned depends upon which rules are in effect: while 736 MEPs will be elected under the Nice rules, this number would have increased to 751 if the Lisbon Treaty were in force.
A further change that Lisbon would have brought was an increase to the powers of Parliament, including powers over the appointment of the President of the European Commission.[78] It had been suggested by some that political parties could run with candidates for the Commission President;[79] with leaders now linking the post to elections and that convention having being enshrined in the Constitution, further encouraging the possibility.[80]
In 2007, it emerged that current Commission President José Manuel Barroso would likely seek a second term,[19] which he confirmed on 19 July 2008,[81] and he received the backing of French President Nicolas Sarkozy.[82] In beginning to formalise the emerging party-political nature of the office, in early 2009 the centre-right People's Party backed Barroso as their candidate and the centre-left socialists opposed, however they did not put forward their own formal candidate.[83]
Observer MEPs
The following 18 parties are likely to receive seats for observers when the Lisbon treaty goes into force. On 23 June an intergovernmental conference (IGC) of EU member states amended a protocol attached to the Lisbon treaty on transitional arrangements. Those transitional arrangements were originally envisaged as taking the total number of MEPs from 785 to 751 for the 2009 elections. The amended text says that the protocol “shall enter into force if possible on 1 December 2010”. Germany is allowed to retain its three additional MEPs until the next elections in 2014. Officials and diplomats hope that national parliaments can ratify the changed protocol by then.[84] Note that this table already includes the grouping changes announced by the parties and reflected in the section below. It is not clear how each member state decides who will get an additional seat in the European Parliament.[85][86]
| Country | National Party | Political Group | Cite |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | SPÖ | S&D | [33] |
| Austria | BZÖ | NI | [33] |
| Bulgaria | SK | EPP | [87] |
| France | ? | ? | [88] |
| France | ? | ? | [88] |
| Italy | ? | ? | [89] |
| Latvia | PS | EPP | [89] |
| Malta | PL | S&D | [89] |
| Netherlands | PVV | NI | [90] |
| Poland | PSL | EPP | [89] |
| Slovenia | SDS | EPP | [89] |
| Spain | PP | EPP | [89][91] |
| Spain | CiU | EPP | [89][91] |
| Spain | PSOE | S&D | [89][91] |
| Spain | PSOE | S&D | [89][91] |
| Sweden | S | S&D | [92] |
| Sweden | PP | Greens-EFA | [92] |
| United Kingdom | Con | ECR | not definitive yet[89] |
Party changes
Traditionally, realignment between the different political groups and European political parties occurs in the runup to the election and in the time between the election and the first sitting of the European Parliament, when the political groups are constituted; the first sitting of the EP elected in 2009 is set for 14 July 2009.[93]
New rules regarding the minimum number of members needed for a political group will come into effect following the 2009 election. The PES and EPP–ED had initially proposed to raise the limit for groups in the EP from 20 MEPs and one fifth of member states to 30 MEPs and a quarter of member states, which would effectively close down UEN (only MEPs from six countries) and I/D (only 22 MEPs). All five smaller groups (UEN and I/D plus ALDE, Greens–EFA and GUE–NGL) protested against these proposed changes.[94] The proposal was voted down 15 to 14 in committee, and in an eventual compromise, new rules were approved in plenary on 9 July 2008 which require 25 MEPs from at least a quarter of the member states (i.e. seven member states).[95] Although UEN and I/D still fail to meet the basic requirements of the new rules, the adopted compromise also included a provision allowing the continued existence of a group which had fallen below the threshold, but only if it still had members from at least a fifth of the member states and only if it had been founded at least a year before dropping below the threshold; if there is "sufficient evidence" of the abuse of this provision, it need not be applied.[96]
Fate of AEN/UEN
The Union for Europe of the Nations (UEN) political group, a rump body that traced its ancestry back to its origins as a Gaullist ideological alignment, was not reconstituted following this election. The associated Alliance for Europe of the Nations (AEN) party lost MEPs to other groupings.
The largest single contributor of MEPs to the UEN group, the Italian National Alliance, merged with Silvio Berlusconi's Forza Italia party into The People of Freedom (PdL) on 29 March 2009.[97] PdL inherited FI's membership in the EPP; a single list of PdL candidates will be run in 2009 which would then take their seats in the EPP-ED (or a purely EPP) group, substantially reducing the potential MEPs that a UEN group could draw upon.[98] This move will come after a series of attempts by National Alliance to abandon more staunchly national-conservative and Eurosceptic parties and move towards the moderate European centre-right, including a previous application for EPP membership.
National Alliance shares the group presidency with Ireland's Fianna Fáil, a centre-right party that joined the European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party (ELDR) on 16 April 2009 with the intent of moving to the European Parliament's Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe (ALDE) group.[99] As a longtime proponent of European integration, FF had been even more openly uncomfortable about its European affiliation, with former leader Bertie Ahern often distancing his party from the right-wing positions of his groupmates and describing UEN as purely a "technical arrangement." Fianna Fáil very nearly joined ALDE during the group reshuffle after the 2004 European elections, and had also previously explored seeking membership in ELDR.[100][101] Current leader Brian Cowen announced that FF would join ELDR and ALDE after the election on 27 February 2009 and a resolution supporting such a move was passed by the party membership two days later.[102][103] FF's leader in the European Parliament, Brian Crowley, criticised this decision and stated that FF might lose its position and influence due to the change, as Crowley currently enjoys a number of privileges as UEN leader which he can use to further FF's policies, but which he would lose if FF were to move to ALDE instead.[104]
A third significant source of UEN's MEPs is Poland. Self-Defense of the Republic of Poland and League of Polish Families enjoy very little popular support and failed to stay in parliament in the Polish 2007 election,[105]
AEN/UEN is also under threat from a potential new group led by members of the European Democrats (see below), who are attempting to woo its remaining members away. Law and Justice of Poland has been reported to be ready to do just this.[106]
The looming disappearance of AEN/UEN also has had repercussions for Independence/Democracy, as it was also a suitor for those parties of UEN left groupless. Lega Nord and the Danish People's Party opted for this and launched the new Europe of Freedom and Democracy group with what was left of Ind/Dem after the election.[107] The ChristianUnion, formerly member of Ind/Dem left for the new European Conservatives and Reformists group.
Movement for European Reform
The Conservatives and Ulster Unionists of the United Kingdom, together with the Czech Civic Democrats might leave the European Democrats (effectively dissolving it through lack of members, as only one Italian will be left - and has not been reelected), which is currently allied to the European People's Party (EPP); instead, these parties will form a new parliamentary grouping based on the Movement for European Reform (MER).[108]
Although the Conservatives alone have the minimum required number of MEPs at 19, they would still need to join with parties or independents from six other countries to formally create a group. There has been speculation that Polish Law and Justice would join the proposed grouping, although it expressed its support for the continuance of the UEN,[109] it is reportedly keen to join MER.[106]
Another possible party is the Latvian TB/LNNK, also currently aligned with AEN. There are also numerous independents that might join the group. The most optimistic estimates suggest MER could become the third largest group in the Parliament.[110]
The Conservative Party reiterated its intention to leave the EPP in March 2009. The new group may be called "European Conservatives" or "European Conservatives and Reformists".[111][112]
The foundation of the European Conservatives was deemed unlikely to threaten the EPP's position as the largest grouping in the European Parliament,[113] with Hix, Marsh, and Vivyan predicting there being less than 1% probability of the EPP suffering such a reverse.[114]
Socialist Group in the European Parliament
The newly born Democratic Party in Italy is still discussing about the group its members will join in the European Parliament. The party was officially created in 2007 from the merger of the two biggest centre-left Italian parties, Democrats of the Left and The Daisy (La Margherita), whose members in the EP joined PES and ALDE respectively after the 2004 elections. Although pushing hard for a unification of all European progressive reformists, and therefore for a merger between PES and ALDE, it is likely that the two parliamentary groups will continue living as separate bodies, forcing the Italian Democratic Party to stay alone in the Parliament. In last general elections, it gained 33.7% of votes.
It was reported on 13 May 2009 that the Group of the PES in the European Parliament would likely choose a new name to accommodate the Democratic Party, with the most likely name being "Alliance of Socialists and Democrats for Europe".[115]
The Cypriot Democratic Party (DIKO), which had previously sat with ALDE but was not a member of any European political party, announced prior to the election that it would want to join the Socialist Group in the European Parliament, though this has yet to be approved by the PES.[116]
On 12 June 2009, it was officially confirmed that the group of the PES would be known as "Alliance of Socialists and Democrats for Europe" (ASDE) in the new parliament,[117][118] though this name was changed to "Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats" (S&D) when the group was officially founded on 23 June 2009.[119]
Parliamentary groups 2009

The following changes occurred, which makes the make-up of the groups as follows:
- ALDE, Greens-EFA and EUL-NGL continue to exist.
- ECR is constituted
- PES becomes part of S&D.
- EPP-ED becomes EPP again
- I/D is replaced by EFD
- UEN is disbanded.
| Political group[120]
Country |
EPP | S&D | ALDE | Greens-EFA | ECR | EUL-NGL | EFD | NI | MEPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 6 (ÖVP) | 4 (SPÖ) | 2 (Grüne) | 3 (Martin) 2 (FPÖ) |
17 | ||||
| Belgium | 3 (CD&V) 1 (CDH) 1 (CSP-EVP) |
3 (PS) 2 (SP.A) |
3 (OpenVLD) 2 (MR) |
1 (Green!) 2 (Ecolo) 1 (N-VA) |
1 (LDD) | 2 (VB) | 22 | ||
| Bulgaria | 5 (GERB) 1 (SDS/DSB) |
4 (BSP) | 3 (DPS) 2 (NDSV) |
2 (Attack) | 17 | ||||
| Cyprus | 2 (DISY) | 1 (EDEK) 1 (DIKO) |
2 (AKEL) | 6 | |||||
| Czech Republic | 2 (KDU–ČSL) | 7 (ČSSD) | 9 (ODS) | 4 (KSČM) | 22 | ||||
| Denmark | 1 (C) | 4 (A) | 3 (V) | 2 (F) | 1 (N) | 2 (O) | 13 | ||
| Estonia | 1 (IRL) | 1 (SDE) | 1 (RE) 2 (KE) |
1 (Tarand) | 6 | ||||
| Finland | 3 (Kok.) 1 (KD) |
2 (SDP) | 3 (Kesk.) 1 (SFP) |
2 (Vihr.) | 1 (PS) | 13 | |||
| France | 29 (UMP) | 14 (PS) | 6 (MoDem) | 14 (E-É) | 5 (FG) | 1 (Libertas) | 3 (FN) | 72 | |
| Germany | 34 (CDU) 8 (CSU) |
23 (SPD) | 12 (FDP) | 14 (Grüne) | 8 (Linke) | 99 | |||
| Greece | 8 (ND) | 8 (PASOK) | 1 (Greens) | 2 (KKE) 1 (SYRIZA) |
2 (LAOS) | 22 | |||
| Hungary | 14 (Fidesz-MPP) | 4 (MSZP) | 1 (MDF) | 3 (Jobbik) | 22 | ||||
| Ireland | 4 (FG) | 3 (Lab) | 3 (FF) 1 (Harkin) |
1 (SP) | 12 | ||||
| Italy | 29 (PdL) 5 (UDC) 1 (SVP) |
21 (PD) | 7 (IdV) | 9 (LN) | 72 | ||||
| Latvia | 2 (PS) 1 (JL) |
1 (TSP) | 1 (LPP/LC) | 1 (PCTVL) | 1 (TB/LNKK) | 1 (LSP) | 8 | ||
| Lithuania | 4 (TS-LKD) | 3 (LSDP) | 1 (DP) 1 (LRLS) |
1 (LLRA) | 2 (TT) | 12 | |||
| Luxembourg | 3 (CSV) | 1 (LSAP) | 1 (DP) | 1 (Déi Gréng) | 6 | ||||
| Malta | 2 (PN) | 3 (PL) | 5 | ||||||
| Netherlands | 5 (CDA) | 3 (PvdA) | 3 (VVD) 3 (D66) |
3 (GL) | 1 (CU) | 2 (SP) | 1 (SGP) | 4 (PVV) | 25 |
| Poland | 25 (PO) 3 (PSL) |
6 (SLD) 1 (UP) |
15 (PiS) | 50 | |||||
| Portugal | 8 (PSD) 2 (CDS) |
7 (PS) | 2 (CDU) 3 (BE) |
22 | |||||
| Romania | 10 (PD-L) 3 (UDMR) 1 (Băsescu) |
11 (PSD-PC) | 5 (PNL) | 3 (PRM) | 33 | ||||
| Slovakia | 2 (SDKÚ-DS) 2 (KDH) 2 (SMK) |
5 (Smer) | 1 (LS-HZDS) | 1 (SNS) | 13 | ||||
| Slovenia | 2 (SDS) 1 (NSi) |
2 (SD) | 1 (LDS) 1 (Zares) |
7 | |||||
| Spain | 23 (PP) | 21 (PSOE) | 1 (CDC) 1 (EAJ-PNV) |
1 (ERC) 1 (ICV) |
1 (IU) | 1 (UPyD) | 50 | ||
| Sweden | 4 (M) 1 (KD) |
5 (S) | 3 (FP) 1 (C) |
2 (MP) 1 (PP) |
1 (V) | 18 | |||
| United Kingdom | 13 (Lab) | 11 (LD) | 2 (GPEW) 2 (SNP) 1 (PC) |
24 (Con) 1 (UCUNF) |
1 (SF) | 13 (UKIP) | 2 (BNP) 1 (DUP) 1 (Con) |
72 | |
| Total | 265 | 184 | 84 | 55 | 54 | 35 | 32 | 27 | 736 |
Parliament President
In the first vote of the new Parliament Jerzy Buzek (EPP, Poland) was elected Parliament President, winning with 555 votes to 89 votes over his opponent Eva-Britt Svensson (EUL-NGL, Sweden).[121]
The two candidates were:
- For the right of centre European People's Party, former Polish PM Jerzy Buzek was nominated by his group EPP-ED and supported by the PES and ALDE groups.
- On the left, Swedish MEP Eva Britt Svensson was nominated by her group EUL-NGL.
MEPs voted in a secret ballot on Tuesday morning 14 July.[122]
The two largest groups in Parliament, the EPP-ED and PES, agreed to share the post of President of the European Parliament as they have done for all but two terms of Parliament. The first half of the term will be taken by Jerzy Buzek MEP of the EPP. He is the first MEP from Eastern Europe to hold the post. He pass it over to Martin Schulz MEP, the current leader of PES.[123] The deal got support form The ALDE group (their candidate Graham Watson dropped out from the race).[124]
The other official candidate was Eva-Britt Svensson, nominated from EUL-NGL.[125] She campaigned with the slogan "a different voice". She was the first MEP from Sweden to candidate to the position.
References
- ↑ "European Parliament". Europarl.europa.eu. 2008-05-21. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?language=EN&type=IM-PRESS&reference=20080520IPR29479. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ UK Office Calendar
- ↑ "CIA — The World Factbook — European Union". Cia.gov. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ee.html#People. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ (Dutch)Telegraaf.nl 1500 votes on the Antilles
- ↑ In the order of the time zones: Saint Pierre and Miquelon, French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Barthélemy, Saint Martin, French Polynesia
- ↑ Delfi As. "Муниципальные выборы". Rus.delfi.lv. http://rus.delfi.lv/news/elections2009/municipal/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ Department of the Official Report (Hansard), House of Commons, Westminster (2008-11-04). "House of Commons Hansard Debates from 4 November 2008 - Local Government Motion". Publications.parliament.uk. http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm200708/cmhansrd/cm081104/debtext/81104-0008.htm#08110438000010. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "News — Department of the Environment, Heritage & Local Government". Environ.ie. http://www.environ.ie/en/LocalGovernment/Voting/News/MainBody,19443,en.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Philippa Runner (2009-02-24). "EUobserver". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/27664. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Honor Mahony. "EUobserver". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/27926/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
- ↑ "Home". Predict09.eu. http://www.predict09.eu/default/en-us.aspx. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
- ↑ "Home". Predict09.eu. 2009-06-04. http://www.predict09.eu/default/en-us.aspx. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ Europa.eu, EP Press Release 16/12/08
- ↑ Waterfield, Bruno (2009-05-22). "Eighteen 'phantom' MEPs will do no work for two years". London: Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/eu/5362190/Eighteen-phantom-MEPs-will-do-no-work-for-two-years.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "MaltaMedia.com". Maltamediaonline.com. 2009-06-10. http://www.maltamediaonline.com/?p=9305. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ Peter, Laurence (2009-05-25). "Europe | Europe may elect 'virtual MEPs'". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/8066946.stm. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ history of the European Green Party at europeangreens.org
- ↑ "★ Europe United — Start — News". Europeunited.eu. http://europeunited.eu/modules/start/. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 European politics to get more political, EU Observer 27/06/07
- ↑ "Kuneva to lead Liberal list in Bulgaria | EU — European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. 2009-04-27. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/kuneva-lead-liberal-list-bulgaria/article-181673. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ "Commissioners tipped to run in EU elections | EU — European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/commissioners-tipped-run-eu-elections/article-179169. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "Bulgarian EU Commissioner turns down EP seat — EU Business News". EUbusiness.com. 2009-07-10. http://www.eubusiness.com/news-eu/1247224653.98/. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "European elections 2009". RCN. http://www.rcn.org.uk/europeanelections2009. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Nursing UK and abroad". RCN. http://www.rcn.org.uk/nursing. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "EU elections 2009 · Campaigning in Europe · BOND". Bond.org.uk. 2009-03-30. http://www.bond.org.uk/pages/eu-elections.html. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Campaigning in Europe · Europe · BOND". Bond.org.uk. http://www.bond.org.uk/pages/eu_campaigning.html. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ EU wants to dress up 2009 elections on TV, EUobserver.com Accessed 26 February 2007
- ↑ "MEPs outline plans to boost EU parliament election turnout". theparliament.com. 2007-11-27. http://www.theparliament.com/EN/News/200711/e880c0b0-dd40-445f-9999-14d7fa81edb3.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ FAQ's on Parliament's election campaign, Europarl-Website
- ↑ Since 23 June 2009, S&D
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Austria". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/austria_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Martin hängt FPÖ ab" (in (German)). Orf.at. http://orf.at/090607-39069/index.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 "SPÖ büßt weiteren Sitz in EU-Parlament ein" (in (German)). Orf.at. http://www.orf.at/090609-39192/39194txt_story.html. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Belgium". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/belgium_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Bulgaria". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/bulgaria_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ M3 Web. "Bulgaria: Bulgaria with 38% Voter Turnout in 2009 European Elections - Exit Poll - Novinite.com - Sofia News Agency". Novinite.com. http://www.novinite.com/view_news.php?id=104439. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Cyprus". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/cyprus_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Κύπρος: Μεγάλη η αποχή στις ευρωεκλογές 2009". Express.gr. http://www.express.gr/news/world/177938oz_20090606177938.php3. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for the Czech Republic". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/czech_republic_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Overall results of voting". volby.cz. http://volby.cz/pls/ep2009/ep11?xjazyk=EN. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "Europavalg". Danmarks Radio. http://www.dr.dk/Nyheder/Temaer/2009/Europa/?v. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Estonia". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/estonia_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Estonian National Electoral Committee: Results of the European Parliament Election, 2009". Vvk.ee. http://www.vvk.ee/ep09/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ Hääletamis- ja valimistulemus (Estonian)
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Finland". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/finland_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for France". Results of the 2009 European Elections. http://www.20minutes.fr/article/330869/Elections-europeennes-Europeennes-Les-gagnants-les-perdants-dans-chaque-circonscription.php. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "TNS Sofres, leader français des études marketing et d'opinion". Tns-sofres.com. http://www.tns-sofres.com/europeennes2009/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Germany". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/germany_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Greece". Results of the 2009 European Elections. Ministry of Internal Affairs. http://ekloges-prev.singularlogic.eu/e2009/pages/index.html?lang=en. Retrieved 2009-10-06.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Hungary". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/hungary_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Index - Külföld". Index.hu. 2008-06-08. http://index.hu/kulfold/eu/2009/valasztas/ep-valasztas_2009/gyozott_a_fidesz_kiesett_az_szdsz_bejutott_a_jobbik/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "RTÉ News: European Elections 2009". Rte.ie. http://www.rte.ie/news/elections/european/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "Ministers' meeting a charade, says new MEP Higgins". The Irish Times. 19 June 2009. http://www.irishtimes.com/newspaper/world/2009/0619/1224249121582.html. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Italy". Results of the 2009 European Parliament election. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/italy_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Italy". Results of the 2009 European Parliament election. Italian Ministry of the Interior. http://elezioni2009.interno.it/europee/ET0.htm. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Latvia". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/latvia_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "В Латвии более половины избирателей приняли участие в выборах в Европарламент - Новости России - ИА REGNUM". Regnum.ru. http://www.regnum.ru/news/1172796.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Lithuania". http://www.vrk.lt/2009_ep_rinkimai/output_en/rezultatai_daugiamand_apygardose/rezultatai_daugiamand_apygardose1turas.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Luxembourg". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/luxembourg_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Malta". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/malta_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European Parliament Elections - Official Results". Department of Information (Malta). 2009-06-09. http://www.doi.gov.mt/EN/elections/2009/EU_Parlelections/eu_parl1.asp. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for the Netherlands". Dutch election committee. http://www.kiesraad.nl/nl/Verkiezingen/Verkiezingen-Overzicht/Uitslag_verkiezing_van_de_leden_van_het_Europees_Parlement_van_4_juni_2009.html.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Poland". Results of the 2009 European Elections (98,9% of votes). PKW. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/poland_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "PO zabiera europosła PSL Policzyli 98,9 proc. głosów - Informacje - portal TVN24.pl - 08.06.2009". Tvn24.pl. 08/06/2009. http://www.tvn24.pl/-1,1604126,0,1,po-zabiera-europosla-psl--policzyli-98-9-proc-glosow,wiadomosc.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Portugal". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/portugal_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Romania". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/romania_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Slovakia". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/slovakia_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Smer vyhral, mimoparlamentné strany neuspeli | Eurovoľby 2009". volby.sme.sk. http://volby.sme.sk/c/4878625/smer-vyhral-mimoparlamentne-strany-neuspeli.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Slovenia". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/slovenia_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Volitve v Evropski parlament 2009". Volitve.gov.si. http://volitve.gov.si/ep2009/udel_ve.html. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Spain". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/spain_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Official results for Spain". Spanish Ministry of the Interior. http://resultados2009.mir.es/99PE/DPE99999TO.htm. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "European election results 2009 for Sweden". Valmyndigheten. http://www.val.se/val/ep2009/slutresultat/rike/. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ↑ "European Election Results 2009, UK Results". BBC News. 2009-04-19. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/shared/bsp/hi/elections/euro/09/html/ukregion_999999.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-02.
- ↑ "26th Conservative MEP elected - in Northern Ireland - thetorydiary". Conservativehome.blogs.com. 2009-06-08. http://conservativehome.blogs.com/thetorydiary/2009/06/26th-conservative-mep-elected-in-northern-ireland.html. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "Results of the 2009 European election". Results of the 2009 European Elections. TNS opinion. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/index_en_txt.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ "Composition of the 2009 European Parliament (historical data)". http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/hist_composition_en.html. Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- ↑ Europa website. "The Union's institutions: The European Parliament". http://europa.eu/scadplus/constitution/parliament_en.htm. Retrieved 2007-06-28.
- ↑ Size shouldn't matter commentisfree.guardian.co.uk 10/01/07
- ↑ Too much champagne, not enough leadership opendemocracy.net 10/07/03
- ↑ Honor Mahony (2008-07-19). "Barroso admits he wants to be EU commission president for a second time". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/26513/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Honor Mahony. "Sarkozy backs Barroso for second go as EU commission president". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/26475/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ EU Socialists disagree with early choice of commission chief, EU Observer
- ↑ EuropeanVoice.com: ‘Phantom' MEPs to have votes from December
- ↑ Valentina Pop (2009-11-25). "Parliament to get extra observer MEPs from 12 countries". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/29048. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ EuropeanVoice.com: Spain wants seats for ‘phantom' MEPs
- ↑ "Решение № ЕП-256/09.06.2009 на ЦИКЕП" (in (Bulgarian)). ЦИКЕП. http://cikep2009.eu/?resh=260. Retrieved 2009-06-12.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 "Coulisses de Bruxelles" (in (French)). http://bruxelles.blogs.liberation.fr/coulisses/2009/06/où-sont-passés-les-73e-et-74e-eurodéputés-français-.html.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 89.3 89.4 89.5 89.6 89.7 89.8 89.9 "France to pick 'phantom MEPs' from parliament". EurActiv. http://www.euractiv.com/en/future-eu/france-pick-phantom-meps-parliament/article-187928. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "PVV krijgt vijfde zetel in Europarlement" (in Dutch). http://www.nu.nl/algemeen/2098919/pvv-krijgt-vijfde-zetel-in-europarlement.html.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 91.2 91.3 "Spanish Royal Decree 482/2009, issuing election writs for the European Parliament" (in Spanish). Spanish Official Gazette. 2009-04-14. http://www.boe.es/aeboe/consultas/bases_datos/doc.php?coleccion=iberlex&id=2009/06164. Retrieved 2009-06-10. The decree establishes that any additional MEP seats created by the application of the Treaty of Lisbon before the next election are to be filled by appointing the individuals that would have won the new seats had the original election been held with the new number.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Pirate party's next goal - become weigher in national parliament" (in Swedish). Aftonbladet. 2009-06-08. http://www.aftonbladet.se/nyheter/euvalet/article5337619.ab. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
- ↑ "EU offered timetable for Barroso's successor | EU — European Information on EU Treaty & Institutions". EurActiv.com. 2009-03-20. http://www.euractiv.com/en/future-eu/eu-offered-timetable-barroso-successor/article-180444. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Andrew Duff (2008-05-27). "European Parliament's political diversity at risk". EUobserver.com. http://euobserver.com/9/26216/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Honor Mahony. "New rules to make it harder for MEPs to form political groups". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/26468/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ European Parliament increases threshold to form a political group
- ↑ "Berlusconi creates rightist bloc". BBC News. 2009-03-28. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7967932.stm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "Berlusconi win raises hopes, fears in Brussels — EUbusiness.com — business, legal and economic news and information from the European Union". Eubusiness.com. 2008-04-15. http://www.eubusiness.com/news-eu/1208269038.8. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Taylor, Simon (2009-04-17). "Fianna Fáil joins Parliament's liberal grouping | Policies | EU governance | Parliament". European Voice. http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/2009/04/fianna-f%C3%A1il-joins-parliament%27s-liberal-grouping/64640.aspx. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ European Political Parties (Part II: the parties) [with Poll]: Alliance for the Europe of the Nations eurotrib.com 28/12/06
- ↑ FF ‘may switch to the Liberals’—Eh, since when are FF liberals? irishelection.com 19/12/06
- ↑ "Full Text: Taoiseach Brian Cowen at the official Opening of 72nd Fianna Fáil Ard Fheis — Part 1 | Fianna Fáil". Fiannafail.ie. http://www.fiannafail.ie/feature/entry/full-text-taoiseach-brian-cowen-at-the-official-opening-of-72nd-fianna-fail/. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "Red-carpet treatment as Cowen gets into bed with liberals". The Irish Times. 2009-03-20. http://www.irishtimes.com/newspaper/world/2009/0320/1224243123715.html. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "UEN leader voices doubts over Fianna Fáil's move to Liberals | EU — European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. 2009-03-09. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/uen-leader-voices-doubts-fianna-fail-move-liberals/article-180022. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ KB (2007-09-01). "News from Poland — Poll: elections good for Civic Platform and Law and Justice". Poland.pl. http://www.poland.pl/news/article,Poll:_elections_good_for_Civic_Platform_and_Law_and_Justice,id,291198.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ 106.0 106.1 "Isaby, Jonathan — Eurosceptic group in EU strengthens". London: Blogs.telegraph.co.uk. 2008-01-29. http://blogs.telegraph.co.uk/politics/threelinewhip/jan08/eueurosceptic.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Brunsden, Jim. "New Eurosceptic group formed in Parliament | Policies | EU governance | Parliament". European Voice. http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/2009/06/new-eurosceptic-group-formed-in-parliament/65361.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ In full: Cameron Euro declaration BBC News 13/07/06
- ↑ Q&A: The Tories and the EPP BBC News 13/07/06
- ↑ "The Tories and their EU allies 11/07/06". BBC News. 2006-07-11. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/4665818.stm. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ Leigh Phillips. "EUobserver". EUobserver. http://euobserver.com/9/27762/?rk=1. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "Will UK Tories return EU Socialists to power? | EU — European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. 2009-03-12. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/uk-tories-return-eu-socialists-power/article-180179. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "New pan-European Eurosceptic alliance takes shape | EU - European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. 2009-06-02. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/new-pan-european-eurosceptic-alliance-takes-shape/article-182769. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "Overall Analysis". Predict09.eu. 2009-06-04. http://www.predict09.eu/default/en-us/european_analysis.aspx. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ "Socialist group to change name after EU elections | EU — European Information on EU Elections 09". EurActiv.com. 2009-05-13. http://www.euractiv.com/en/eu-elections/socialist-group-change-name-eu-elections/article-182251. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Διαμάχη ΔΗΚΟ - ΕΔΕΚ για τη συμμετοχή στους Σοσιαλιστές". Sigma Live. http://www.sigmalive.com/simerini/politics/160952. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ Taylor, Simon. "New alliance emerges in European Parliament | Policies | EU governance | Parliament". European Voice. http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/2009/06/new-alliance-emerges-in-european-parliament/65180.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ AGI.it
- ↑ Taylor, Simon (2009-06-23). "Socialists formalise new alliance | Policies | EU governance | Parliament". European Voice. http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/2009/06/socialists-formalise-new-alliance-/65273.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "Results of the 2009 European Elections". TNS opinion in collaboration with the European Parliament. 2009-07-08. http://www.elections2009-results.eu/en/index_en.html. Retrieved 2009-07-09.
- ↑ "News on the Parliament Website". Europarl.europa.eu. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/expert/infopress_page/008-58064-195-07-29-901-20090713IPR58063-14-07-2009-2009-false/default_en.htm. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "Parliament Website". Europarl.europa.eu. 2009-07-13. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/public/story_page/008-57768-201-07-30-901-20090706STO57748-2009-20-07-2009/default_en.htm. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "Next EP president to be a Pole?". Brusselsblogger.blogactiv.eu. 2008-04-22. http://brusselsblogger.blogactiv.eu/2008/04/22/next-ep-president-to-be-a-pole/. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ↑ "Press Release". Grahamwatsonmep.org. http://www.grahamwatsonmep.org/news/000626/local_mep_watson_withdraws_from_euro_parliaments_presidential_race.html. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
- ↑ "GUE-NGL Press Release". Guengl.eu. http://www.guengl.eu/showPage.jsp?ID=7658&AREA=27&HIGH=1. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
External links
- Section devoted to the election on the European Parliament website
- EurActiv - EU Elections 2009
- NSD: European Election Database - European Parliament Elections
- EU Observer - EU Elections 2009
- Euronews - EU Elections 2009
- Guide to European Elections provided by European Alternatives
- About the European Elections 2009 in Ireland
- EU Election 2009 Coverage on BBC
- Pre-election survey, EU27 and by member state
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||